HYPERTENSION
Definition: a systolic blood pressure above 140 mmhg or a
diastolic pressure above 90 mmhg based on two or more measurements.
Classification:
1. Optimal-
systolic 120 mmhg diastolic 80 mmhg (120/80)
2. Normal-
systolic 130 mmhg diastolic 85 mmhg (130/85)
3. High
normal- systolic 130 to 139 mmhg diastolic 85 to 89 mmhg (130
4. Stage
1- systolic 140 to 159 mmhg diastolic 90 to 99 mmhg
5. Stage
2- systolic 160 to 179 mmhg diastolic 100 to 109 mmhg
6. Stage
3- systolic 180 mmhg or higher diastolic 110 mmhg or higher
Hypertension
is a major RISK FACTOR for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, heart
failure, stroke and kidney failure
I.
ESSENTIAL
(PRIMARY) HYPERTENSION
·
It accounts to
90-95% in the adult population have essential HPN
·
Affects more women
than men, African- American men
Pathophysiology:
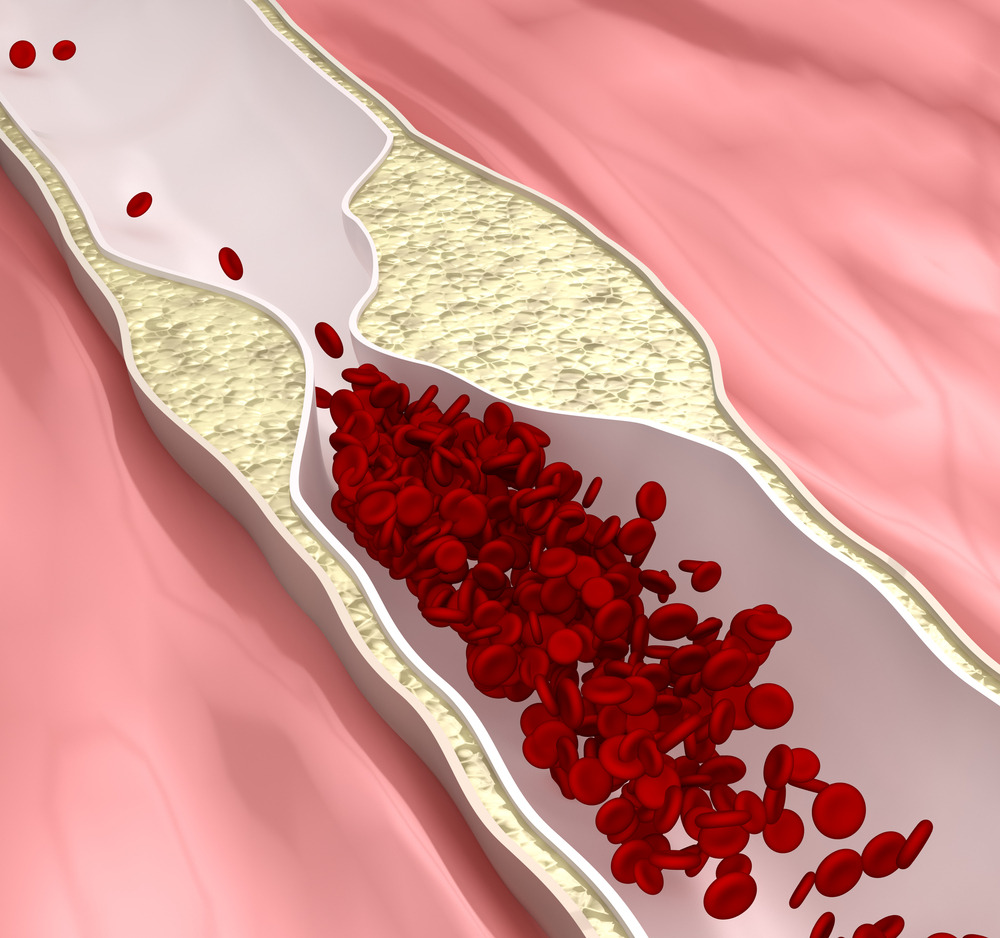 There
is increased in peripheral resistance and or cardiac output secondary to
increased sympathetic stimulation, increased renal sodium reabsorption,
increased rennin angiotensin aldosterone system activity, decreased
vasodilation of the arterioles or resistance to insulin action.
There
is increased in peripheral resistance and or cardiac output secondary to
increased sympathetic stimulation, increased renal sodium reabsorption,
increased rennin angiotensin aldosterone system activity, decreased
vasodilation of the arterioles or resistance to insulin action.
RISK FACTORS:
Obesity,
excessive alcohol intake, overstimulation with coffee, smoking and drug intake.
II.
SECONDARY
HYPERTENSION
·
Characterized by
elevation in BP with a specific cause such as arterial disease, renal disease,
certain medications, tumors and pregnancy hypertension.
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE:
-
History and physical examination
-
Retinal examination
-
Laboratory studies:urinalysis, blood chemistry (sodium, potassium, creatinine,
FBS, total and high density lipoprotein), ECG and echocardiography to assess
left ventricular hypertrophy
-
Special studies: intravenous pyelography, renal arteriography, split renal
function studies, rennin levels, 24 hour urine protein, creatinine clearance.
COMPLICATIONS:
·
Renal Hemorrhage
·
Heart failure
·
Renal insufficiency
and Failure
·
Cardiovascular
Accident (CVA)
·
Transient Ischemic
Attack (TIA)
·
Myocardial
Infarction (MI)
·
Left Ventricular
Hypertrophy
Medical management:
Goal-
to prevent death and complications by achieving and maintaining an arterial BP
below 140/90 mmhg (130/85 mmhg for people with DM or proteinuria> 1 g/24
hrs. whenever possible.
NURSING MANAGEMENT:
I.
ASSESSMENT
·
Assess BP at
frequent intervals , know baseline and note changes in pressure
·
Note the apical and
peripheral pulse rate , rhythm and character
·
Assess symptoms
such as nose bleeds, angina pain, shortness of breath, alterations in vision,
speech or balance (vertigo), headache or nocturia
·
Assess extent to
which HPN has affected patient personally, socially and financially
II.
NURSING
DIAGNOSIS
1.
Deficient knowledge
regarding the relationship between the treatment regimen and control of the
disease process
2.
Noncompliance
related to side effects of prescribed therapy
III.
PLANNING
AND GOALS
·
The major goal of
the patient include understanding the disease process and its treatment,
compliance with the self care program and absence of complications.
IV.
INTERVENTIONS
1.
Increasing
Knowledge
·
Emphasize the
concept of controlling HPN ( with lifestyle changes and medications) rather
than curing it
·
Arrange a
consultation with a dietitian to help patient plan a weight loss
·
Obtain patient
education materials
·
Advise patient to
limit alcohol intake and avoid use of tobacco (smoking)
2.
Monitoring
and Managing Complications
·
Assess all body
systems when patient returns for follow up care
·
Question patient
about blurred vision, spots or diminished visual acuity
·
Report any
significant findings promptly to determine whether additional studies or changes
in medications are required.
V. EVALUATION
Expected
Patient outcomes:
·
Maintains adequate
tissue perfusion
·
Complies with
self-care program
·
Experiences no
complications


I started on COPD Herbal treatment from Ultimate Health Home, the treatment worked incredibly for my lungs condition. I used the herbal treatment for almost 4 months, it reversed my COPD. My severe shortness of breath, dry cough, chest tightness gradually disappeared. Reach Ultimate Health Home via their email at ultimatehealthhome@gmail.com . I can breath much better and It feels comfortable!
ReplyDeleteAfter years of struggling with COPD and finding little to no lasting relief, I decided to try the herbal treatment from NaturePath Herbal Clinic—and it turned out to be one of the best decisions I’ve ever made.
ReplyDeleteWithin just four months, I experienced significant improvements: my breathing became easier, my persistent cough subsided, and the tightness in my chest noticeably lessened. I can now walk longer distances, sleep more peacefully, and enjoy everyday activities without constant fatigue or shortness of breath.
This treatment has truly transformed my quality of life. If you're looking for a natural and effective approach to managing COPD, I wholeheartedly recommend NaturePath Herbal Clinic.
Learn more: www.naturepathherbalclinic.com
After years of battling COPD with little to no lasting relief, I turned to the herbal treatment from NaturePath Herbal Clinic—and it’s one of the best decisions I’ve made.
ReplyDeleteWithin just four months, I experienced noticeable improvements: easier breathing, reduced coughing, and a significant decrease in chest tightness. I'm now able to walk longer distances, sleep more soundly, and enjoy daily activities without constant fatigue or shortness of breath.
This treatment has genuinely transformed my quality of life. If you're seeking a natural and effective solution for COPD, I wholeheartedly recommend NaturePath Herbal Clinic.
Learn more: www.naturepathherbalclinic.com